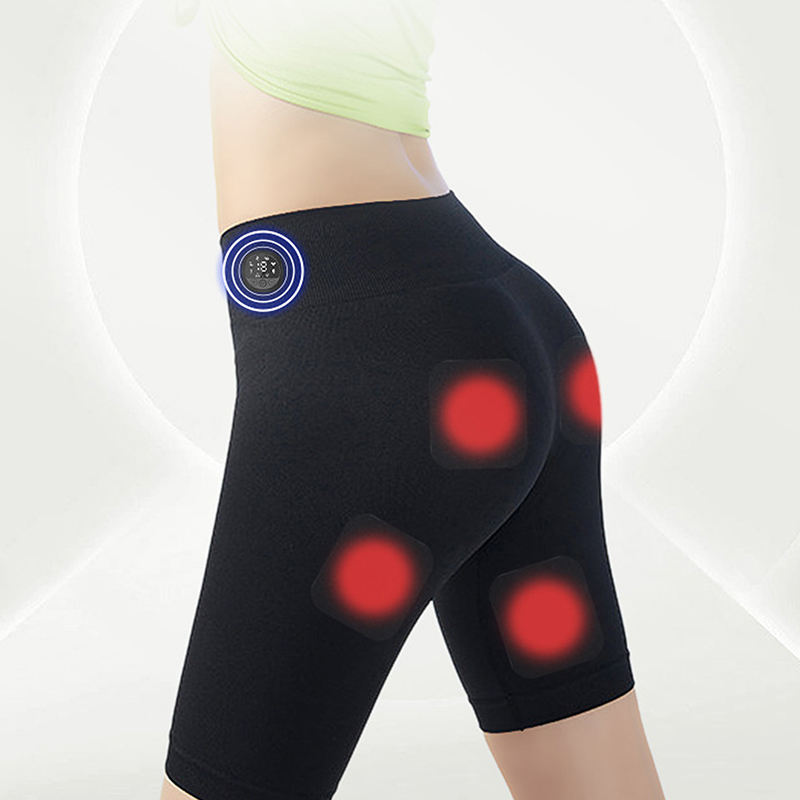
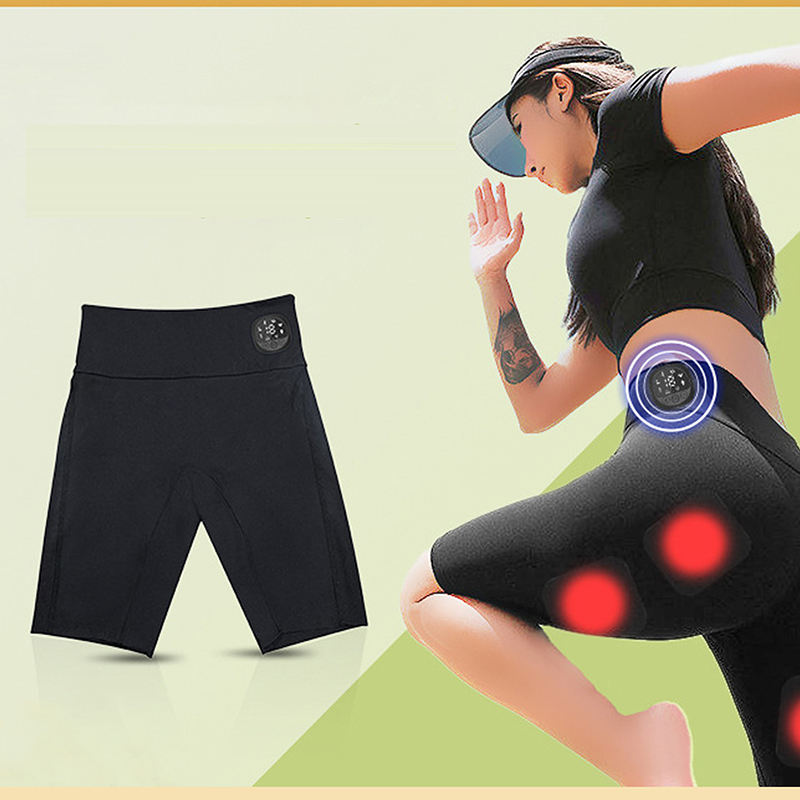
Innovative training technology

EMS Training Pants
EMS Training Pants – Your ideal training partner for running in the forest, at home or in the office!
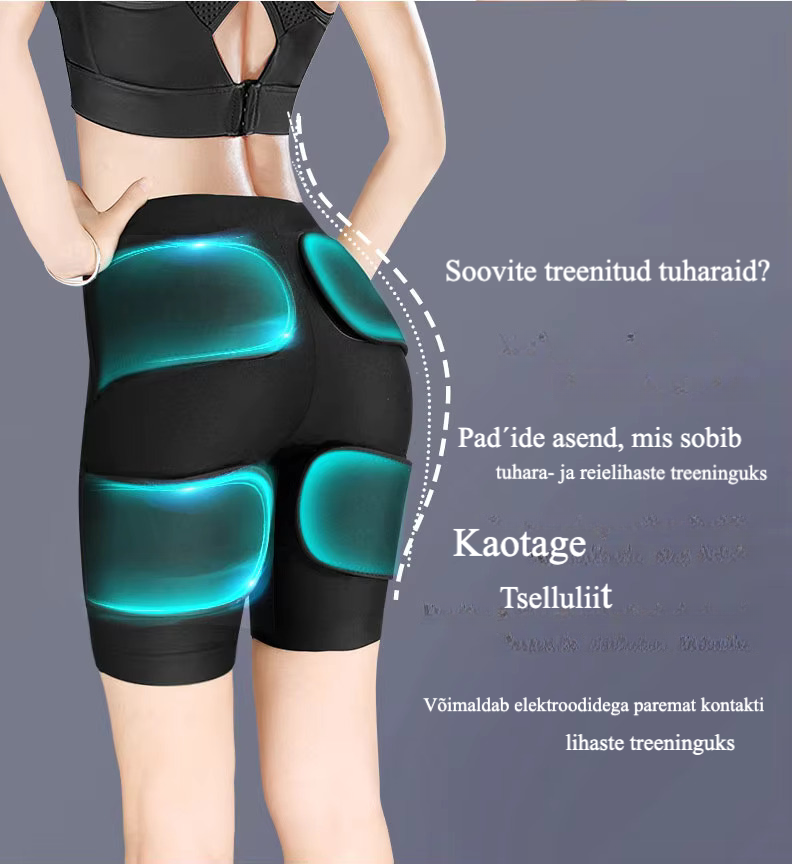
EMS With electrostimulation, you can successfully fight both cellulite and loose skin. Six Infrared-heated “pads” that transmit electrical impulses send impulses to your muscle groups and make your muscles work for you. Ideal for people with a fast-paced lifestyle who want to build muscle and burn calories. The effects of electrostimulation have been scientifically proven and have been used by NASA scientists.
While EMS pants have previously been relatively inaccessible to the general public due to their high price (600 – 800 EUR), we are able to offer good quality EMS pants at a much lower price. If you are not satisfied with our product, you can return it free of charge within 14 days.
137.00€
Payment in three interest-free installments
BEST QUALITY
We offer the best
CONVENIENT PAYMENT
Also installment payment
LONG WARRANTY
Best customer support
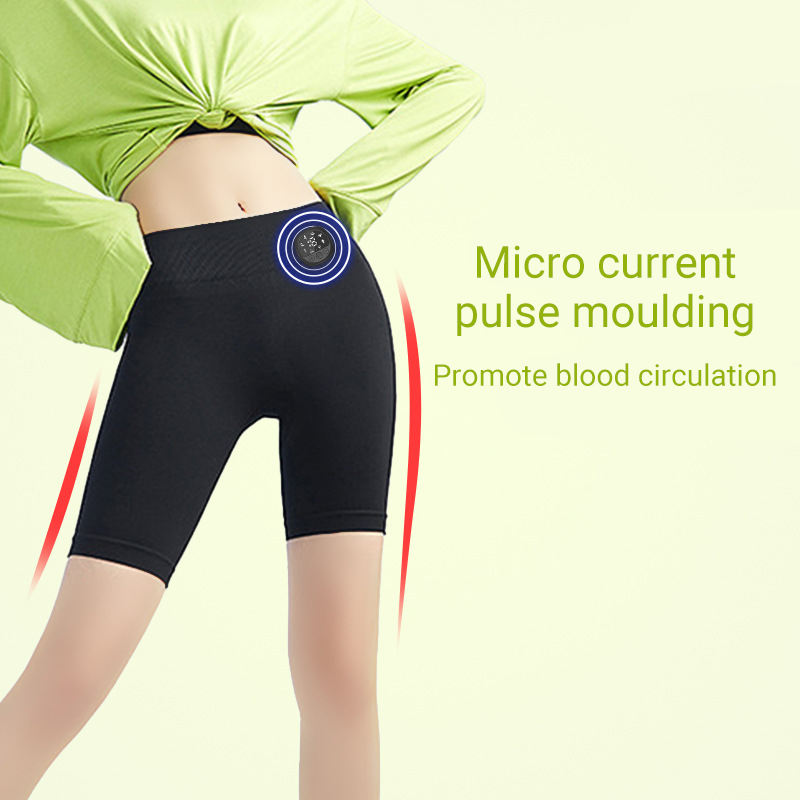
With EMS technology, you'll see training results faster than usual.
Stimulates deep muscles, making the body trim.
A choice of 6 programs will help you achieve your goal!
Relieves muscle tension and pain after exercise.
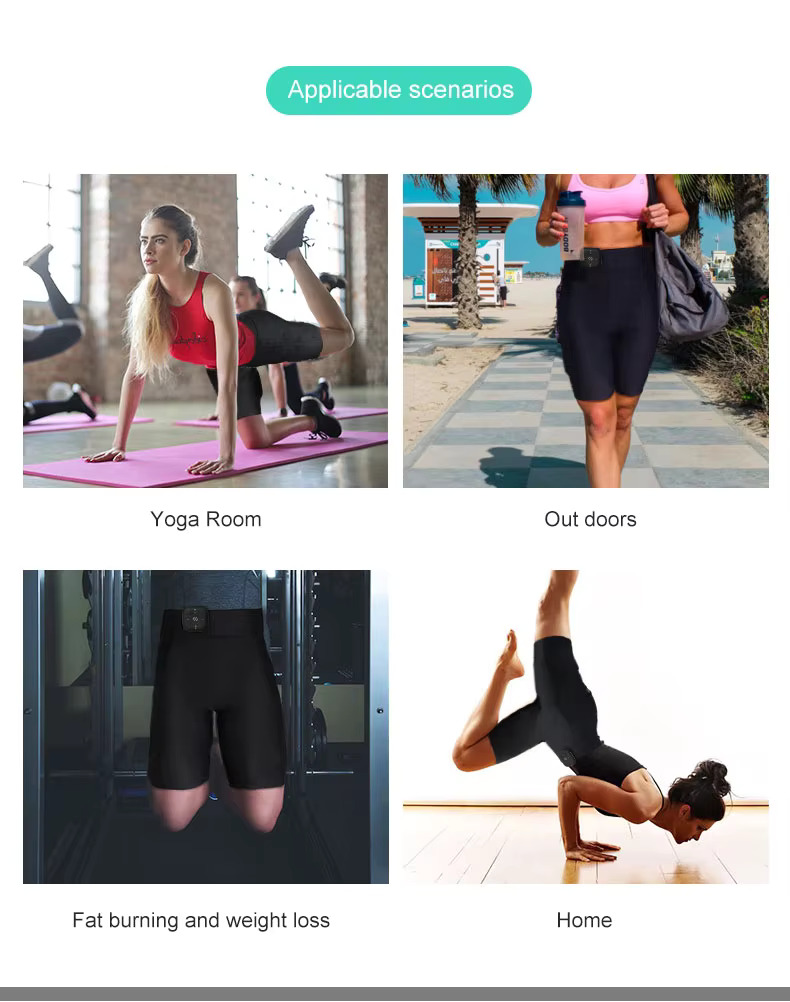
Suitable for running, gym or home workouts.
Effective Training with New Technology!
EMS Training Pants Reduce Cellulite and Trim Muscles
Improve your workouts and feel great EMS Training Pants! EMS pants combine electrical muscle stimulation with infrared heating and a comfortable and stylish design. EMS Training Pants stimulate muscles, burn calories and help you achieve your fitness goals.
- Reduces cellulite
- Accelerates fat burning and helps with weight loss
- Increases muscle tone and shapes the body
- Accelerates recovery after exercise
- Reduces muscle tension and improves blood circulation
- Comfortable and suitable for various workouts
- Easy to use and maintain
Why use:
Select EMS Training Pants and achieve your fitness goals faster and more effectively!
+ MEDICAL RESEARCH – The effect of electrical muscle stimulation on deep muscle activation and physical performance.
The EMS Training Pants study was conducted on 41 students in South Korea. You can read the full English-language medical study of the EMS Pants download here
The study was conducted by:
Hyun-Joon Yoo, MD, PhDa, Sangsoo Park, PhDb, Sejun Oh, PT, PhDc, Munjeong Kang, MDa, Yongha Seo, MAd, Byung Gon Kim, PhDe, Sang-Heon Lee, MD, PhDa,*
Summary: Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) activates muscles using an electrical current, resulting in involuntary muscle contractions. The aim of the study was to evaluate the immediate effects of wearing “EMS Training Pants” on healthy non-athletic adults, compared to conventional training on healthy non-athletic adults.
Methods: This was a randomized, controlled, parallel-group crossover study. Forty-one healthy young middle-aged volunteers were recruited and randomly assigned to two groups: EMS Sport + EMS (S+E) and Sport (S) groups. All participants completed a 30-minute strength training program, three times a week for 8 weeks, consisting of core exercises. In addition, the S+E group received EMS during the training session, which stimulated bilateral abdominal, gluteal, and hip adductor muscles. As the primary outcome measure, we assessed changes in muscle thickness, including abdominal, gluteal, and hip muscles, using ultrasound. Muscle thickness was measured both at rest and in the contracted state. Secondary outcomes assessed physical performance. Functional movement scores consisted of the McGill Cardiac Stability Test, the Hip Muscle Performance Test, and body composition analysis. All assessments were performed at baseline and at the end of the test.
Results: 39 participants completed the study (S+E group = 20, S group = 19). After completing the training, the (Sport+EMS) group showed more efficient contraction in most of the muscles assessed. Resting muscle thickness did not differ significantly between the groups. However, contracted muscle thickness in the S+E group was greater than in the S group (p < 0.05). Physical performance and body composition did not differ significantly between the two groups. No complications related to the intervention were reported during the study.
Conclusion: EMS appears to be a safe and reasonable way to improve fitness in healthy individuals. Abbreviations: AL = adductor longus, BIA = bioelectrical impedance analysis, EMS = electrical muscle stimulation, EO = external oblique, FMS = functional movement screen, GMed = gluteus medius, IO = internal oblique, RA = rectus abdominis, STEMS = application of electrical muscle stimulation to conventional exercise training, TrA = transverse abdominis. Keywords: abdominal muscle, electrical stimulation, exercise, muscle contraction, strength training
HJY and SP-Company contributed equally to the study. This study was supported by the ICT Creative Consilience Program (IITP-2022-2020-0-01819) of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea and supervised by the Institute of Information and Communication Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP-2023-2020-0-01819). The study was funded by the manufacturer of the EMS device (SP – EMS COMPANY, Seoul, South Korea).
Clinical trial registration identifier: KCT0007569. Additional digital content is available for this article.a Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, School of Global Sports Studies, Korea University Sejong Campus, Institute of Human Behavior and Genetics, Associate Research Center, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea.
Association, Seoul, Republic of Korea, e QOLFIT Training Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.* Correspondence: Sang-Heon Lee, Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University Anami Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, 73, Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Republic of Korea (e-mail: spinelee@gmail.com). Copyright © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CCBY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. How to cite this article: Yoo HJ, Park S, Oh S, Kang M, Seo Y, Kim BG, Lee SH. Effects of electrical muscle stimulation on deep muscle activation and physical performance in non-athletic adults: a randomized controlled trial. Medicine2023; 102:4(E32765). Received: December 4, 2022 / Final received: January 5, 2023 / Accepted: January 5, 2023http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.00000000000032765
1 Medicine®
• Medicine (2023) 102:4
1. Introduction: Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) has long been used as a complementary method of full-body training. [3,4] It artificially activates muscles through various electrical impulses delivered to the muscles via electrodes. As a result, the impulses trigger involuntary muscle contractions, which produce similar muscle contractions and relaxations as during conventional exercise, but without the strain.. [5] Specifically, it was designed to facilitate passive activation of a large number of motor muscles and induce synchronous contraction of muscle fibers, with the goal of increasing or maintaining muscle mass. [6–8] Recent advances in EMS technology have led to the development and implementation of relatively inexpensive and portable EMS devices for both home and commercial users. Previous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of EMS on muscle function and physical performance in a variety of populations, including healthy young adults, the elderly, and patients with muscles that are underperforming due to trauma. (This is the case for the gluteal muscles in wheelchair users, for example.)
In particular, EMS is a supportive and effective rehabilitation method for patients with impaired physical performance or elderly people with low physical activity. Although conventional strength training is the most recommended for muscle mass gain, people who attend traditional gyms are often discouraged by a fast pace of life or low motivation. In these situations, EMS offers the opportunity to increase adherence to an exercise program[10] and improve patients’ body composition and physical strength. [4] Researchers have reported that EMS improves quadriceps strength and lower limb function in frail older patients with acute heart failure,[11] preserves muscle mass and function in patients with mobility impairment,[12] improves balance and reduces the risk of falls in the elderly,[13] reduces deltoid atrophy after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair,[14] and improves quadriceps strength and reduces pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis. [15] However, there is limited research on the effectiveness of EMS, especially in intensive care patients, which requires further research. [8,16]
EMS training has also been widely used in healthy and fit individuals and has been applied to competitive athletes. [17] Some studies have investigated the effects of EMS training on elite athletes, such as rugby, ice hockey, and basketball players, and have reported positive effects on muscle-related outcomes. [18–20] In addition, EMS studies have been conducted in untrained individuals. In recent studies, EMS application can effectively activate the superficial abdominal muscles[21] and increase the cross-sectional area of the lateral abdominal wall and rectus abdominis, as well as lumbopelvic control in healthy individuals. [22] In addition, Nishikawa et al. demonstrated that EMS can induce different distributions of quadriceps muscle activation from 50% and 70% maximal voluntary contractions, as measured by surface electromyography. [23] A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that it appears to have positive effects on muscle mass and strength parameters, but not on body fat mass. [4] However, the reported effects of EMS are partly compromised by factors such as the pre-trained status of the subjects, the lack of standardization of methods, or the intervention protocols. For example, a recent study compared the effects of EMS, conventional strength training, and EMS with conventional exercise (STEMS) on elbow flexion or muscle thickness after 8 weeks. Despite many previous studies, it is reasonable to assume that EMS should not be considered a substitute for conventional exercise training per se, as exercise itself not only improves muscle function but also has positive effects on endothelial function, cardiopulmonary fitness, and cognitive function. [24] The aim of this study was to evaluate the immediate clinical effects of STEMS compared to conventional exercise in healthy non-athletic adults by analyzing muscle thickness, various physical abilities, and body composition over an 8-week period of physical training. To obtain more objective results We conducted a randomized, controlled trial among groups of similar age groups using well-controlled training. In addition, we analyzed the effects of EMS on 3 aspects: physical performance, muscle thickness, and body composition. We hypothesized that STEMS would have additional advantages over conventional ST, as EMS may induce additional muscle fiber recruitment and produce greater changes after training.
2. Methods: This study was a single-blind (outcome assessor), prospective, randomized controlled trial using a parallel-group design conducted at a single center from January 2022 to February 2022. Forty-one healthy young volunteers were recruited and randomized into 2 groups: a group (n = 21) that received 8 weeks of strengthening training with EMS (S + E group) and a group (n = 20) that received 8 weeks of strengthening training alone (S group). A computer-generated random assignment list was used and the randomization results were blinded to the assessors. The primary outcome measure was changes in ultrasound muscle thickness, including abdominal, gluteal, and hip muscles. Secondary outcomes assessed changes in physical performance and body composition. All assessments were performed twice: before the intervention and after the 8-week intervention.
2.1. Participants: The sample size was calculated using Gpower 3.1. An effect size of 0.25, a probability of error of 0.05, and a power of 0.90 were defined as 38 participants. Considering the dropout rate of 10%, we recruited 41 healthy subjects (male = 17, female = 24). Inclusion criteria were as follows: age 20–25 years, no competitive sports, no spinal surgery or persistent low back pain, no medical conditions affecting muscle metabolism such as myopathy, and no medical history that would be affected by EMS, such as epilepsy or pacemaker insertion. All participants provided written informed consent before participation. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University Anami Hospital (2021AN0557). The CONSORT diagram is shown in Figure 1.
2.2. Strength training protocol: During the intervention period, all participants performed 30 minutes of strength training 3 times a week (Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) at the Yangon University gym for 8 weeks. Each training program included an additional 5 minutes of warm-up and cool-down periods with a 30-second rest period between each set. The first 2 weeks of training focused on core stabilization training, and the remaining 6 weeks of training focused primarily on core strengthening. Specifically, the first 2 weeks focused on controlling the contraction and relaxation of the core muscles with open kinetic exercises. We then gradually increased the intensity of the training with closed kinetic exercises, such as planks, in weeks 3–5. Finally, weeks 6–8 of the training program were used for more functional exercises, such as mini-squats, to engage and maximize the function of the involved core muscles. The intensity of the training was adjusted based on the Borg Category Ratio (CR)-10 scale. [25] The level of perceived exertion was gradually increased from “light” to “very hard” (Borg CR-10 scale “2” to “9”) over the 8-week intervention. The detailed physical training program is described in the table, Supplemental Digital Content http://links.lww.com/MD/I379. Participants were provided with adequate warm-up and cool-down periods before and after exercise. All training sessions were supervised and supervised by a professional athletic trainer.
For further reading, please download the study from here.
EMS Training Pants: How Do They Work?
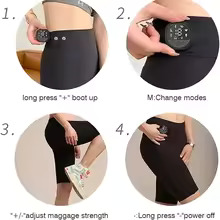
- Prepare yourself for training and make sure the remote control in the pants is charged.
- Make surethat The pants should be tight around the body. The electrostimulation pads target major muscle groups and must be in firm contact with the body.
- Choose the appropriate program: Choose the right program according to your goal: lappetite training, catabolism, fat burning, recovery or auto program.
- Turn on: Press the start button on the remote control of the pants, after which you will feel a gentle stimulation, which means that the muscles are working. You can increase or decrease the intensity of your pre-selected program as desired.
- Enjoy your workout: EMS helps your muscles work harder, so you burn more calories and achieve beautiful buttocks.
DETAILS
More about the product
EMS Workout Pants: Lose Cellulite and Trim Muscles
Get your body in shape with our new EMS pants! They combine electrostimulation and infrared heatto achieve more beautiful skin and a toned buttocks. The ideal companion for running in the forest, gym workouts or just an active lifestyle. EMS pants help you achieve a better figure, smoother skin, and tone your muscles.
Weight loss and muscle training with EMS pants at home, in the gym or outdoors.
Who wouldn't want to be slim, slim and in good shape - but often don't have time to spend a long time in the gym or the energy to force yourself to exercise. With a home EMS device, you can replace your workout with a quick and effective slimming session wherever you want it. A highly effective training method based on electrostimulation, which has gained popularity worldwide and also in Estonia, sends impulses to the muscles to artificially cause muscle tightening and relaxation. The functions are controlled by a remote control attached to the belt, which distributes the impulses to different muscle groups in the pants you put on. Since people and their training are different, you can determine the necessary program and load for the corresponding muscle group yourself.
Why use EMS training pants?
-
EMS – Active muscle stimulation improves blood circulation, reduces cellulite and enhances muscle function. Achieve a deeper and more effective workout, burning more calories.
-
Infrared heat – Gentle infrared heat helps relax muscles, reduce tension, and improve metabolism. Accelerates the elimination of toxins from the body and improves skin elasticity.
-
6 programs – Choose the right program based on your goal – whether it's smoother skin, muscle toning, or fat burning.
-
Effective and practical – Made of high-quality breathable material that is comfortable even during intense workouts. Easy charging and water resistance make use practical and convenient.
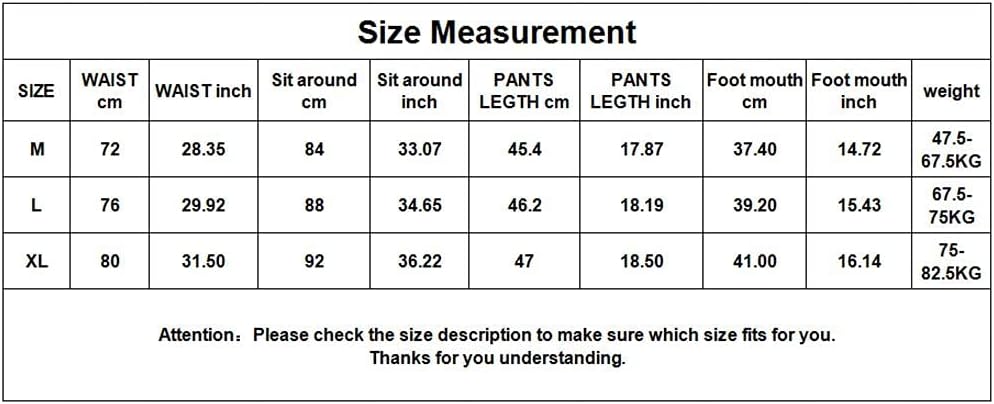
- Select M, L and XL between sizes
EMS training pants are ideal for improving overall body tone, burning fat, tightening skin, and improving exercise results.
Also check out our With infrared mat, which allows you to completely relax both your muscles and your entire body after a workout. Effects of electrical muscle stimulation
Frequently Asked Questions About EMS Training Pants